BMedSci Research: Use of Mobile Technology in Medical Education
BMedSci Research Student | 2014
Award
Winner: Best Overall Poster Presentation
ASME Annual Scientific Meeting 2014, Brighton
Presentions
ASME Annual Scientific Meeting 2014, Brighton
AMEE 2014 Conference, Milan
Abstract
Background
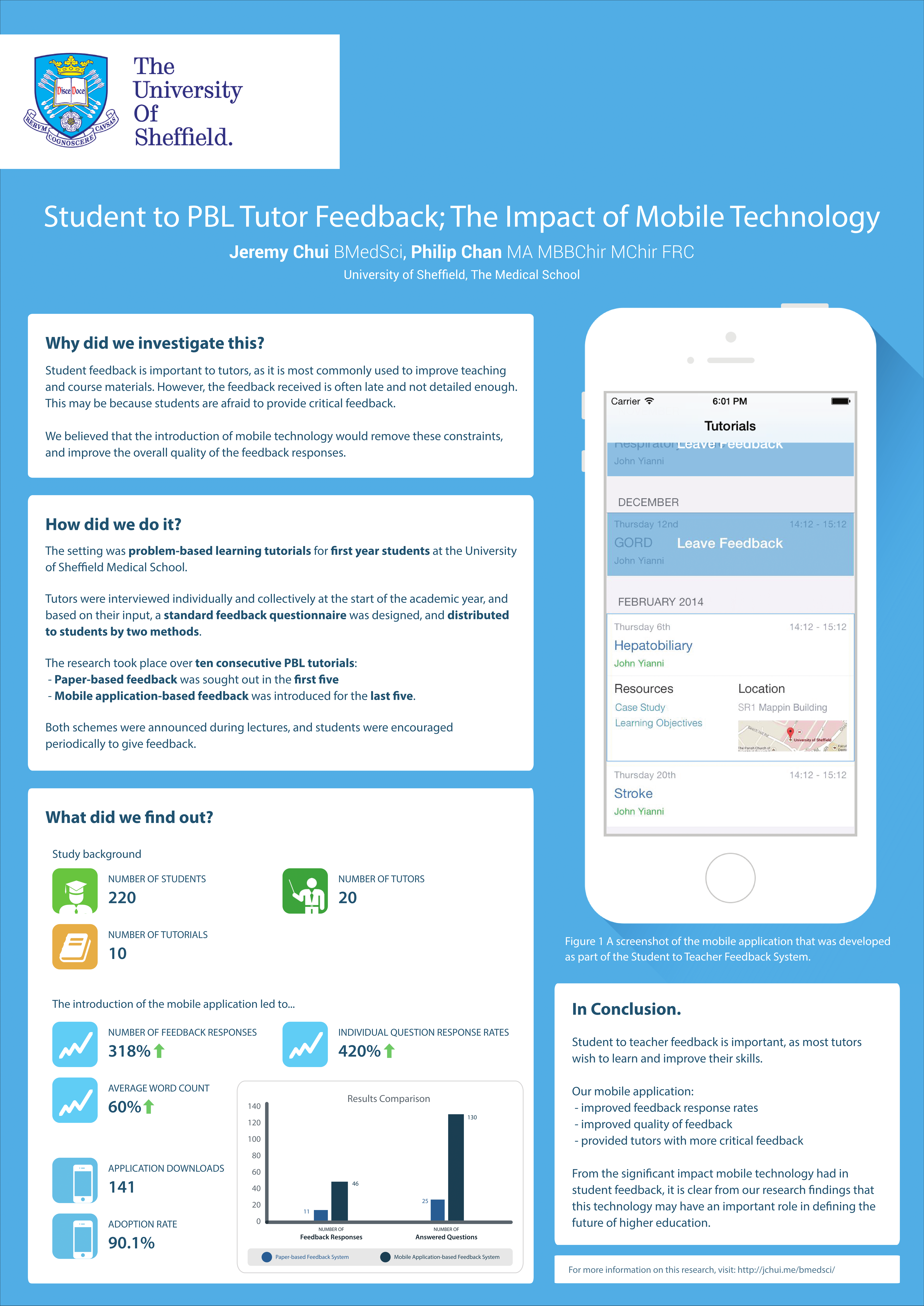
Student feedback to their teachers is an important part of student-centred teaching methods. Course evaluation feedback from students is often late, and not specific to a single tutorial session. We considered that mobile application-based feedback from students might be more timely and relevant.
Method
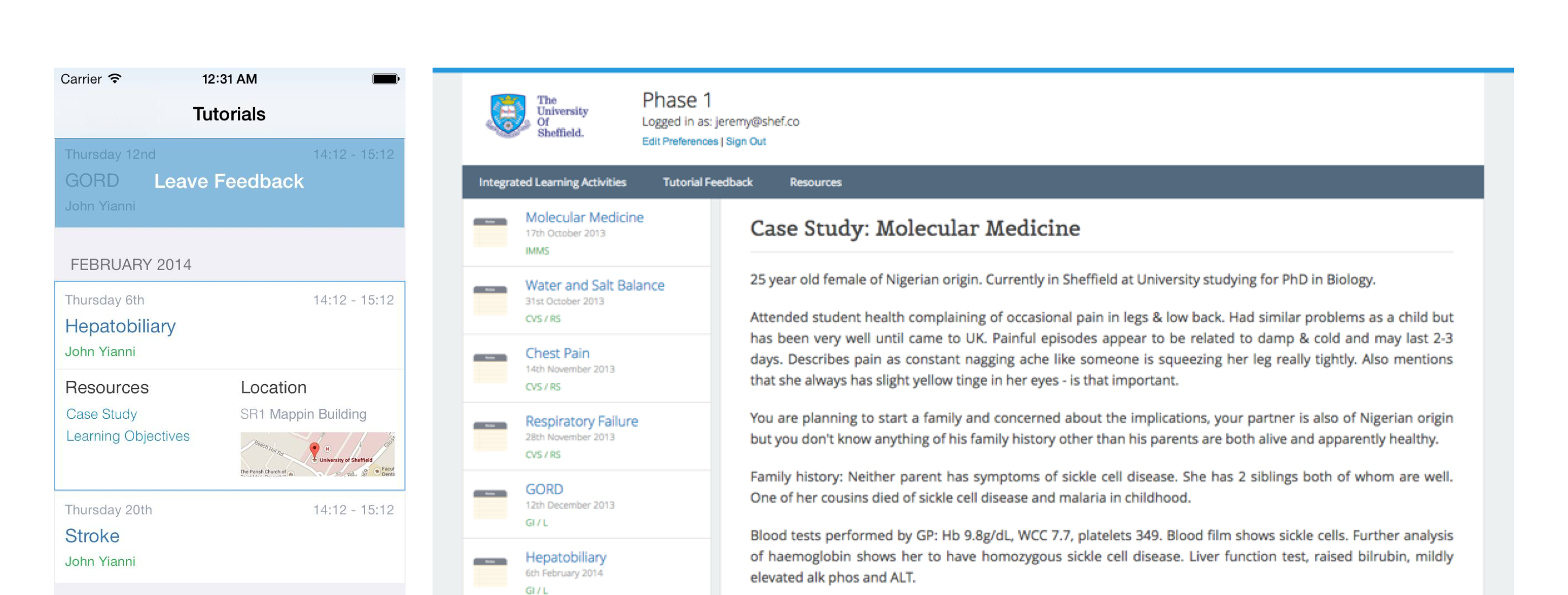
The setting was problem-based learning tutorials for first year students at a single medical school. Tutors were interviewed individually and collectively, at the start of the academic year, and based on their input, a standard feedback questionnaire was designed, and distributed to students by two methods.
Over the period of ten consecutive PBL tutorials, paper-based feedback was sought in the first five, and mobile application-based feedback was introduced for the last five. Both schemes were announced at a lecture, and students encouraged periodically to give feedback. All responses were anonymised, summarized and sent on to individual tutors
Results
We compared response rates and quality of feedback using the two systems. The introduction of the mobile application led to a 330% increase in student to tutor feedback. A total of 141/240 students registered on the website and 108 students downloaded an iPhone specific mobile application.
Conclusion
Student to tutor feedback is important, as most tutors wish to learn and improve their skills. An effective system is beneficial if tutors have to undergo appraisal and revalidation in their teaching role, and can facilitate tutor recruitment. A mobile application method of seeking feedback shows promise in improving rates and quality of feedback.